JavaScript - 1
分析知识模块
变量类型和计算
原型和原型链
闭包和作用域
异步和单线程
思考三个问题
变量类型和计算
1. 值类型和引用类型的区别
js
// 值类型
let a = 100
let b = a
a = 200
console.log(b) // 100js
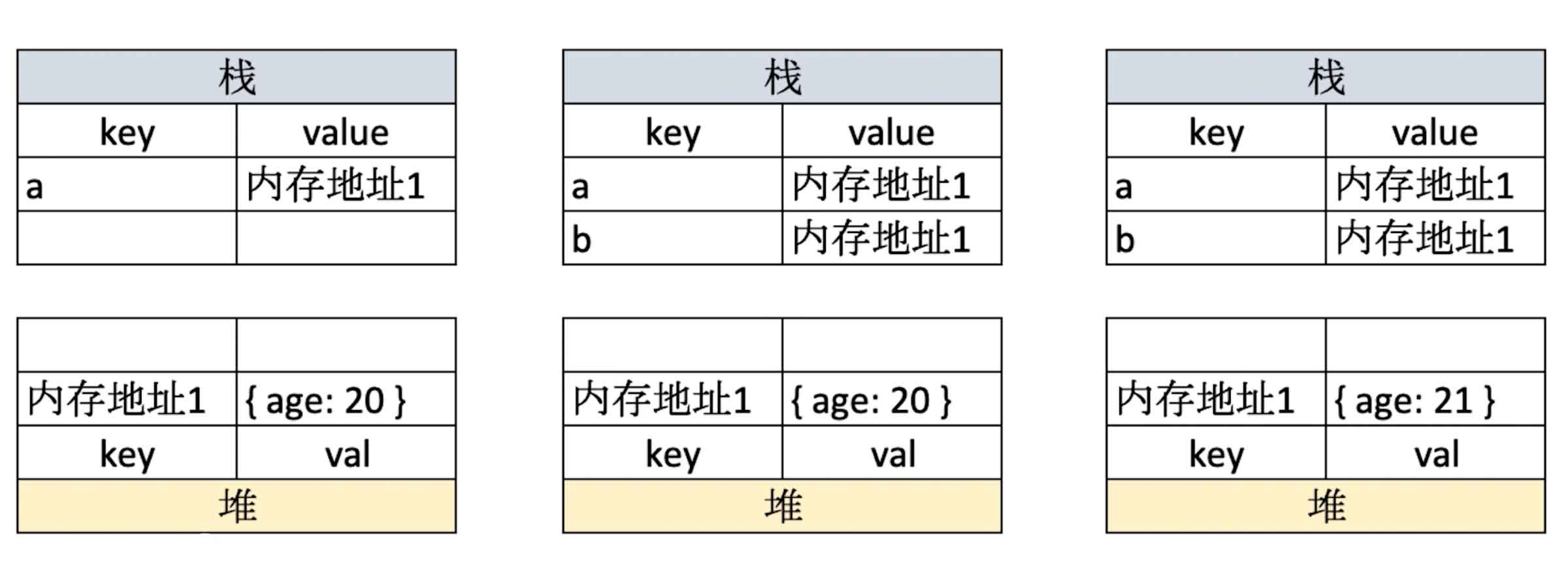
// 引用类型
let a = { age: 20 }
let b = a
b.age = 21
console.log(a.age) // 21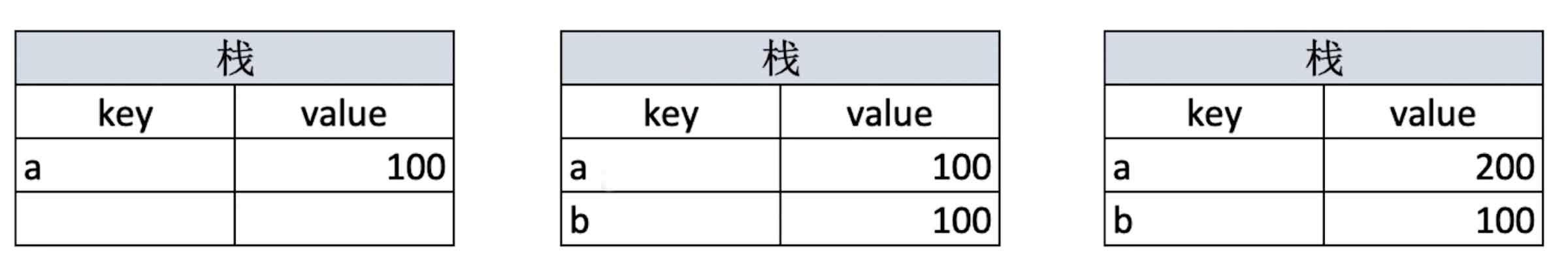
2. 常见值类型和引用类型有哪些
js
// 常见值类型
let a // undefined
const b = 'abc'
const c = 100
const d = true
const e = Symbol('e')js
// 常见引用类型
const obj = { x: 100 }
const arr = ['a', 'b', 'c']
const n = null // 特殊引用类型,指针指向空地址
// 特殊引用类型,但不用于存储数据,所以没有”拷贝、复制函数“说法
function fun() {}js
const obj1 = { x:100 }
const obj2 = obj1
let x1 = obj1.x
obj2.x = 101
x1 = 102
console.log(obj1) // { x: 101 }3. typeof 能判断哪些类型
js
// 判断所有值类型
let a // undefined
const b = 'abc' // 'string'
const c = 100 // 'number'
const d = true // 'boolean'
const e = Symbol('e') // 'symbol'
// 能判断函数
typeof console.log // 'function'
typeof function() {} // 'function'
// 能识别引用类型(不能再继续识别)
typeof null // 'object'
typeof ['a', 'b'] // 'object'
typeof { x: 100 } // 'object'4. 手写深拷贝
js
// 注意判断值类型和引用类型
// 注意判断是数组还是对象
// 核心逻辑:递归
const deepClone = (obj = {}) => {
// obj 是 null, 或者不是对象和数组, 直接返回
if (typeof obj !== 'object' || obj == null) {
return obj
}
// 初始化返回结果
let result
if (obj instanceof Array) {
result = []
} else {
result = {}
}
for (let key in obj) {
// 保证 key 不是原型的属性
if (obj.hasOwnProperty(key)) {
// !! 递归调用 !!
result[key] = deepClone(obj[key])
}
}
return result
}5. 字符串拼接
js
const a = 100 + 10 // 110
const b = 100 + '10' // '10010'
const c = true + '10' // 'true10'6. == 运算符
js
100 == '100' // true
0 == '' // true
0 == false // true
false == '' // true
null == undefined // true7. 何时使用 === 何时使用 ==
js
// 除了 == null 之外,其他一律使用 ===
const obj = { x: 100 }
if (obj.a == null) {}
// 等价于
if (obj.a === null || obj.a === undefiend) {}8. 类型转换和逻辑运算
js
// truly 变量
!!a === true
// falsely 变量
!!a === false
// 以下是 falsely 变量, 除此之外都是 truly 变量
!!0 === false
!!NaN === false
!!'' === false
!!null === false
!!undefined === false
!!false === falsejs
console.log(10 && 0) // 0
console.log('' || 'abc') // 'abc'
console.log(!window.abc) // true9. 小结
值类型和引用类型,堆栈模型, 深拷贝
typeof运算符类型转换,
truly和falsely变量
原型和原型链
前置知识
1. class
js
// 封装
class Student {
constructor(name, num) {
this.name = name
this.num = num
}
sayHi() {
console.log(
`我叫 ${this.name}, 我的学号是${this.num}`
)
}
}
const xialuo = new Student('夏洛', 10086)
console.log(xialuo.name, xialuo.num)
xialuo.sayHi()js
// 继承
class People {
constructor(name) {
this.name = name
}
eat() {
console.log(`${this.name}吃点什么...`)
}
}
// 使用 extends 继承 父类
class Student extends People {
constructor(name, num) {
super(name);
this.num = num
}
sayHi() {
console.log(
`我叫 ${this.name}, 我的学号是${this.num}`
)
}
}
const xialuo = new Student('夏洛', 10086)
console.log(xialuo.name, xialuo.num)
xialuo.sayHi()
xialuo.eat() 重要提示:
class是 ES6 语法规范,由 ECMA 委员会发布- ECMA 只规定语法规则,即我们代码的书写规范,不规定如何实现
- 以上实现方式都是 V8引擎实现方式,也是主流实现方式
2. 类型判断 - instanceof
js
// 类型判断 - instanceof
xialuo instanceof Student // true
xialuo instanceof People // true
xialuo instanceof Object // true
[] instanceof Array // true
[] instanceof Object // true
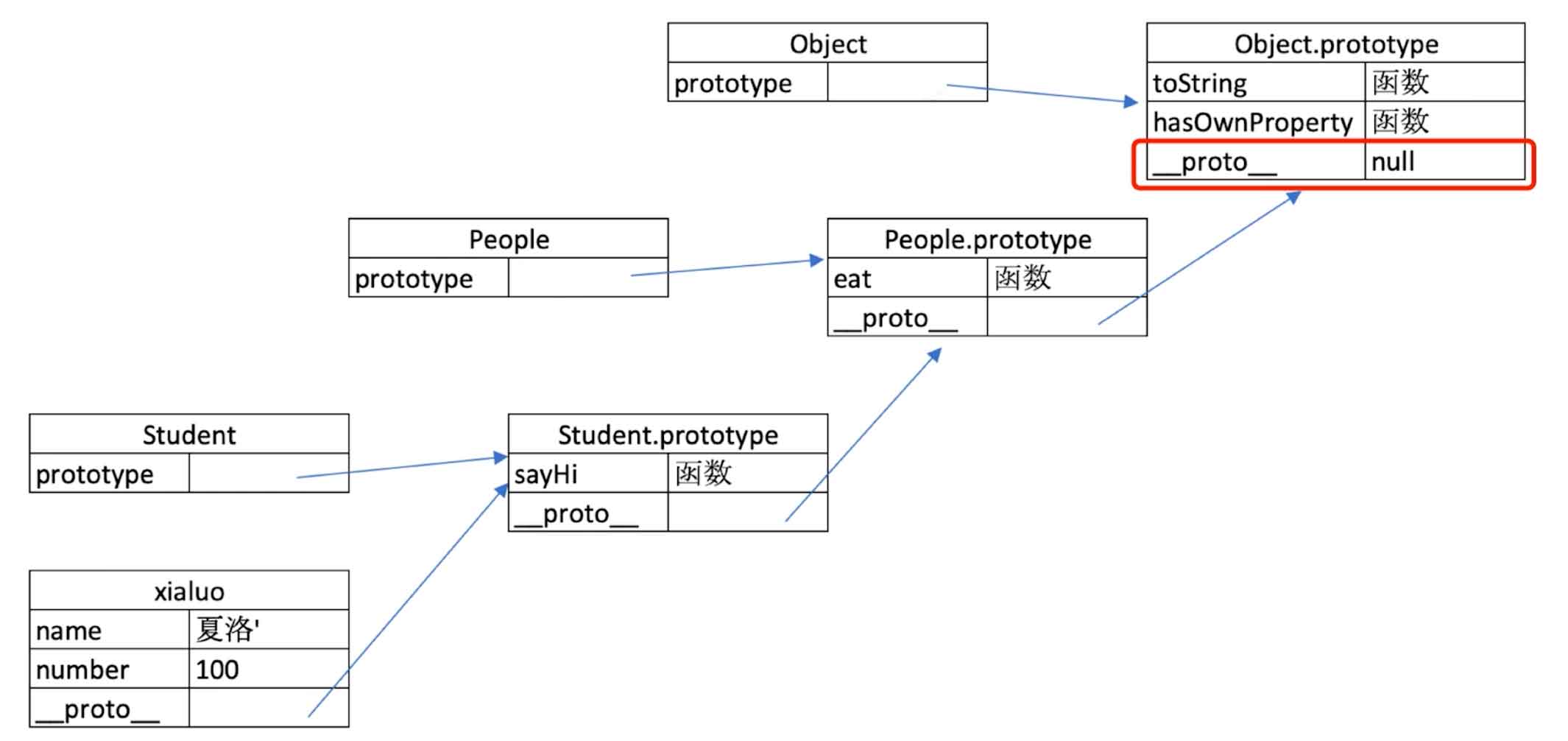
{} instanceof Object // true3. 原型
js
// 原型 *
// class 实际上是函数,可见是语法糖
typeof People // 'function'
typeof Student // 'function'
// 隐式原型和显示原型
console.log(xialuo.__proto__) // 隐式原型
console.log(Student.prototype) // 显式原型
console.log(xialuo.__proto__ === Student.prototype) // true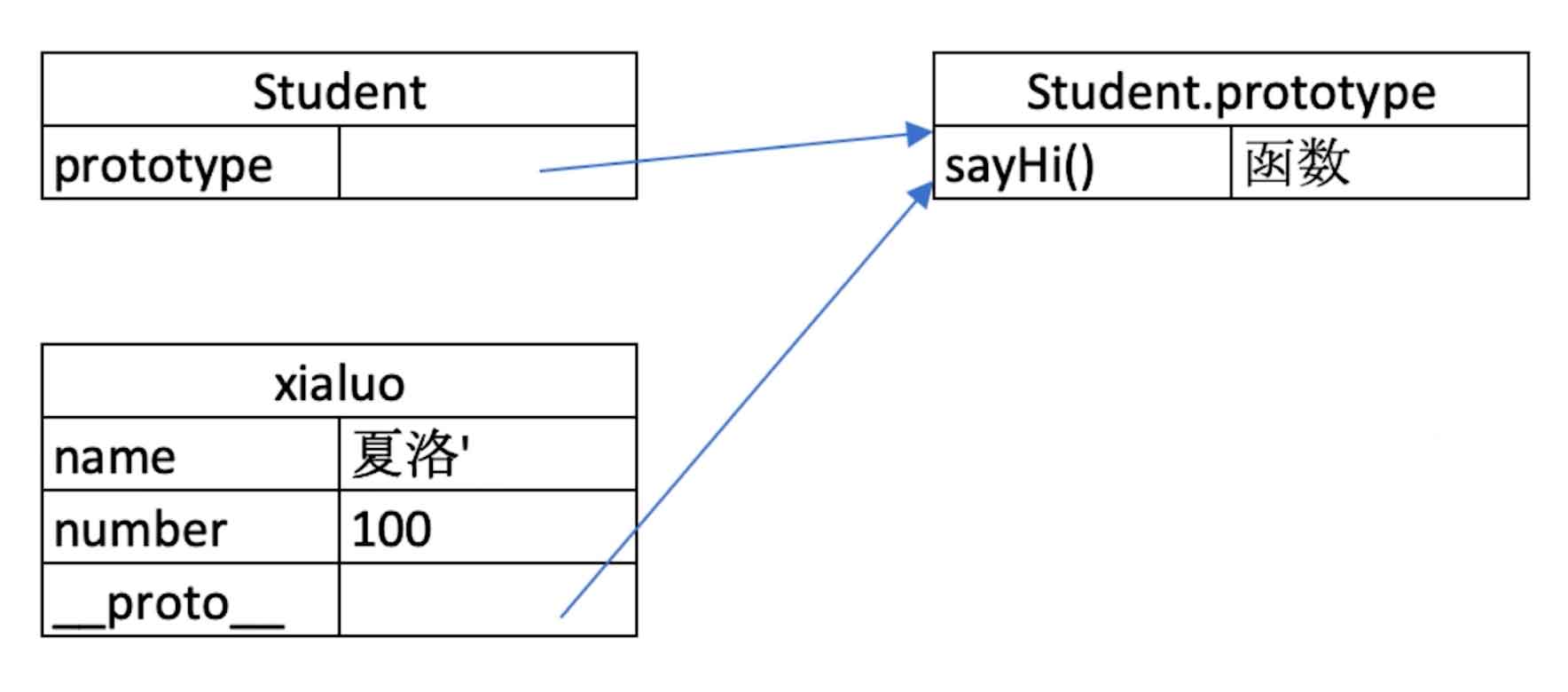
原型关系
- 每个
class都有显示原型prototype - 每个实例都有隐式原型
__proto__ - 实例的
__proto__指向对应class的prototype
基于原型的执行规则
- 获取属性
xialuo.name或执行方法xialuo.sayHi()时 - 先在自身属性和方法中寻找
- 如果找不到则自动去
__proto__中查找
4. 原型链
js
// 原型链 *
console.log(Student.prototype.__proto__)
console.log(People.prototype)
console.log(People.prototype === Student.prototype.__proto__) // true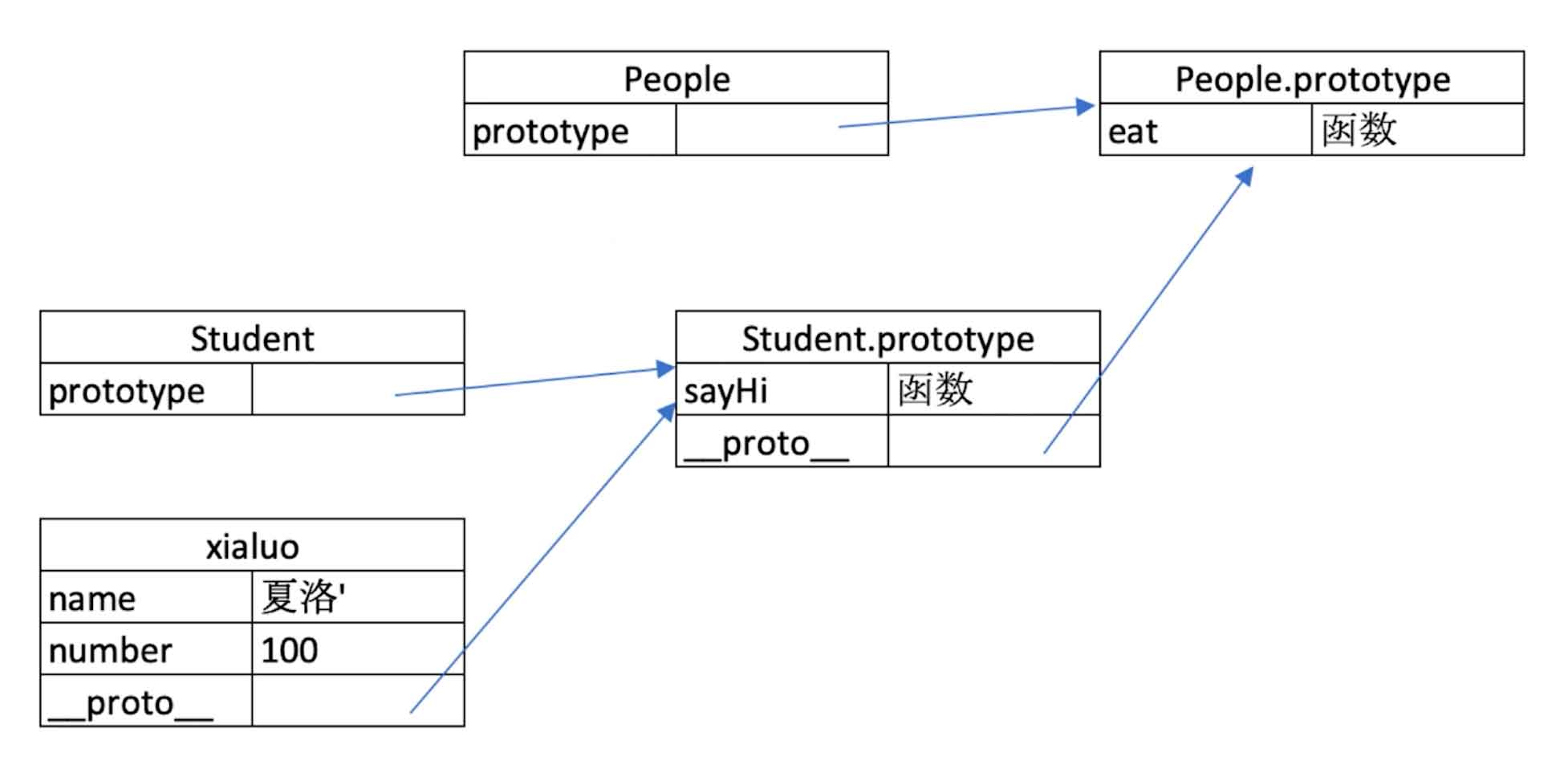
问题:.hasOwnProperty() 哪里来的?
再看 类型判断 - instanceof 是否理解了
1. 如何准确判断一个变量是不是数组
js
a instanceof Array2. 手写一个简易的 jQuery ,考虑插件和扩展性
js
class jQuery {
constructor(selector) {
const result = document.querySelectorAll(selector)
const length = result.length
for (let i = 0; i < length; i++) {
this[i] = result[i]
}
this.length = length
this.selector = selector
}
get(index) {
return this[index]
}
each(fn) {
for (let i = 0; i < this.length; i++) {
const elem = this[i]
fn(elem)
}
}
on(type, fn) {
return this.each(elem => {
elem.addEventListener(type, fn, false)
})
}
// 扩展更多...
}
// 插件
jQuery.prototype.dialog = (info) => alert(info)
// "造轮子"
class myJquery extends jQuery {
constructor(selector) {
super(selector);
}
// 扩展你自己方法...
}
// const $p = new jQuery('p')
// $p.get(1)
// $p.each(elem => console.log(elem.nodeName))
// $p.on('click', () => alert('clicked'))3. class 的原型本质
4. 小结
class和 继承,结合上面手写jQuery的示例来理解insranceof- 原型、原型链:图示 & 执行规则
作用域和闭包
前置知识
1. 作用域
全局作用域
函数作用域
js
let a = 0
function fn1() {
let a1 = 100
function fn2() {
let a2 = 200
function fn3() {
let a3 = 300
return a + a1 + a2 + a3
}
fn3()
}
fn2()
}
fn1()- 块级作用域( ES6 新增)
js
if (true) {
let x = 100
}
console.log(x) // 会报错2. 自由变量
- 一个变量在当前作用域没有定义,但被使用了
- 向上级作用域,一层一层依次寻找,直到找到为止
- 如果全局作用域都没有找到,则报错
xx is not defined
3. 闭包时的作用域
作用域应用的特殊情况,有两种表现:
函数作为参数被传递
函数作为返回值被返回
js
// 函数作为参数
function print(fn) {
let a = 200
fn()
}
let a = 100
function fn() {
console.log(a)
}
print(fn) // 100js
// 函数作为返回值
function create() {
let a = 100
return function () {
console.log(a)
}
}
let fn = create()
let a = 200
fn() // 100 所有的自由变量的查找,是在函数定义的地方,向上级作用域查找,而不是在执行地方
1. this 的不同应用场景,如何取值
- 作为普通函数
- 使用
callbind - 作为对象方法被调用
- 在
class方法中调用 - 箭头函数
this 取什么值是在函数执行时确认的,而不是函数定义时确认的
js
// 普通函数调用
function fn1() {
console.log(this)
}
fn1() // windowjs
// call bind
fn1.call({ x: 100 }) // { x: 100 }
const fn2 = fn1.bind({ x: 200 })
fn2() // { x: 200 }js
// 作为对象方法被调用
const zhangsan = {
name: '张三',
sayHi() {
console.log(this) // this 指向当前对象
},
wait() {
setTimeout(function() {
console.log(this) // this 指向 window
}, 1000)
}
}js
// 箭头函数中调用
const zhangsan = {
name: '张三',
sayHi() {
console.log(this) // this 指向当前对象
},
wait() {
// 箭头函数 this 取上层作用域的值
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(this) // this 指向当前对象
}, 1000)
}
}js
// 在 class 方法中调用
class People {
constructor(name) {
this.name = name
this.age = 20
}
sayHi() {
console.log(this)
}
}
const zhangsan = new People('张三')
zhangsan.sayHi() // zhangsan 对象js
// 在原型中
// 此处代码中 xialuo 参考 原型和原型链 -> 前置知识 -> 1. class -> 继承 代码
console.log(xialuo.__proto__.sayHi())
// 我叫 undefined, 我的学号是 undefined
// 此时 this 指向 xialuo.__proto__ 并非 xialuo
xialuo.sayHi()
// 相当于(可以这么理解,并不完全是)
xialuo.__proto__.sayHi.call(xialuo)2. 手写 bind 函数
js
Function.prototype.bind1 = function () {
// 将参数拆解成数组
const args = Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments)
// 获取 this 数组中第一项
const _this = args.shift()
// fun.bind1(...) 中的 fun
const self = this
// 返回一个函数
return function () {
return self.apply(_this, args)
}
}3. 实际开发中闭包的应用场景
js
// 闭包隐藏数据, 只提供 API
function createCache() {
const data = {} // 闭包中的数据, 被隐藏,不被外界访问
return {
set: function (key, value) {
data[key] = value
},
get: function (key) {
return data[key]
}
}
}
const a = createCache()
a.set('a', 100)
console.log(a.get('a'))4. 创建 10 个 a 标签,点击弹出对应序号
js
let a
for (let i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
a = document.createElement('a')
a.innerHTML = i + '</br>'
a.addEventListener('click', e => {
e.preventDefault()
alert(i)
})
document.body.appendChild(a)
}
// 如果改成
let i, a
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
...
}
// 会是什么结果呢?5. 小结
- 作用域和自由变量
- 闭包:两种常见形式 & 自由变量查找规则
this指向
异步和单线程
前置知识
1. 单线程、同步和异步
javaScript是单线程语言,只能同时做一件事- 浏览器和
nodejs已经支持JS启动 ,如Web Worker JS和DOM渲染共用同一个线程,因为JS可修改DOM结构- 遇到等待(网络请求,定时任务)不能卡住
- 回调
callback函数形式 - 异步不会阻塞代码执行
- 同步会阻塞代码执行
js
// 异步 ( callback 回调函数)
console.log(100)
setTimeout(function() {
console.log(200)
}, 1000)
console.log(300)js
// 同步
console.log(100)
alert(200)
console.log(300)2. 应用场景
- 网络请求,如
ajax图片加载 - 定时任务,如
setTimeout
js
// ajax
console.log('start')
$.get('./data.json', (data) => {
console.log(data)
})
console.log('end')js
// 图片加载
console.log('start')
let img = document.creatElement('img')
img.onload = () => {
console.log('loaded')
}
img.src = './xxx.png'
console.log('end')js
// setInterval
console.log(100)
setInterval(() => {
console.log(200)
}, 2000)
console.log(300)3. callback hell 和 Promise
js
// callback hell
// 获取第一份数据
$.get(url1, data1 => {
console.log(data1)
// 获取第二份数据
$.get(url2, data2 => {
console.log(data2)
// 获取第三份数据
$.get(url3, data3 => {
console.log(data3)
// 还可能有更多
})
})
})js
// Promise
function getData(url) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
$.ajax({
url,
success(data) {
resolve(data)
},
error(err) {
reject(err)
}
})
})
}js
getData(url1).then(data1 => {
console.log(data1)
return getData(url2)
}).then(data2 => {
console.log(data2)
return getData(url3)
}).then(data3 => {
console.log(data3)
}).catch(err => console.err(err))1. 同步和异步的区别是什么
同步和异步的区别
2. 手写 Promise 加载一张图片
js
const waitImg = src => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const img = document.createElement('img')
img.onload = () => {
resolve(img)
}
img.onerror = () => {
reject(new Error(`图片加载失败: ${src}`))
}
img.src = src
})
}
waitImg(url).then(res => {
console.log(res.width, res.height)
return res // 普通对象
}).then(res => {
document.body.appendChild(res)
return waitImg(url2) // Promise 实例
}).then(resp => {
document.body.appendChild(resp)
}).catch(err => {
console.error(err)
})3. 前端使用异步的场景有哪些
应用场景
4. setTimeout 笔试题
js
// 打印顺序是什么?
console.log(1)
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(2)
}, 1000)
console.log(3)
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(4)
}, 0)
console.log(5) // 1 3 5 4 2
// 假设 5 的地方代码执行时间很久,那么输出结果是多少呢?5. 小结
- 单线程和异步,异步和同步区别
- 前端异步的应用场景:网络请求 & 定时任务
Promise解决callback hell