数据结构和算法(下)
一、求一个二叉搜索树的第 k 小值
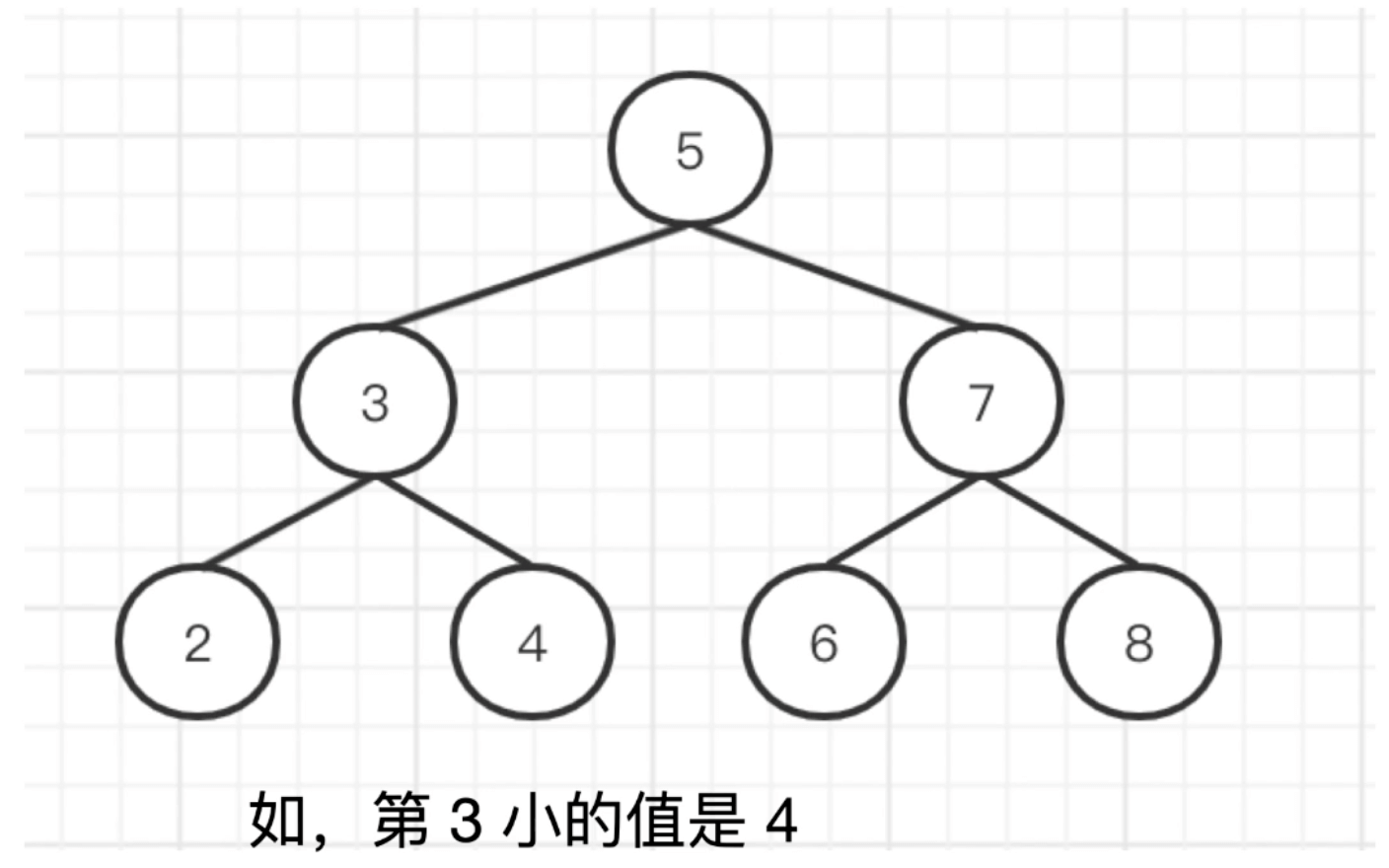
1. 前置知识
- 二叉树( Binary Tree )
- 是一颗树
- 每个节点最多有两个子节点
- 树节点的数据格式
{ value, left?, right? }
- 二叉树的遍历
- 前序遍历:root -> left -> right
- 中序遍历:left -> root -> right
- 后序遍历:left -> right -> root
- 二叉搜索树 BST ( Binary Search Tree )
- left ( 包括其后代 ) value <= root value
- right ( 包括其后代 ) value >= root value
- 可使用 二分法 进行快速查找
2. 代码演示
typescript
interface TreeNode {
value: number,
left: TreeNode | null,
right: TreeNode | null
}
const bst: TreeNode = {
value: 5,
left: {
value: 3,
left: {
value: 2,
left: null,
right: null
},
right: {
value: 4,
left: null,
right: null
}
},
right: {
value: 7,
left: {
value: 6,
left: null,
right: null
},
right: {
value: 8,
left: null,
right: null
}
}
}
/**
* 二叉树前序遍历
* @param node node
*/
// 5 3 2 4 7 6 8
function preOrderTraverse(node: TreeNode | null) {
if (node == null) return
console.log(node.value)
preOrderTraverse(node.left)
preOrderTraverse(node.right)
}
/**
* 二叉树中序遍历
* @param node node
*/
// 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
function inOrderTraverse(node: TreeNode | null) {
if (node == null) return
inOrderTraverse(node.left)
console.log(node.value)
inOrderTraverse(node.right)
}
/**
* 二叉树后序遍历
* @param node node
*/
// 2 4 3 6 8 7 5
function postOrderTraverse(node: TreeNode | null) {
if (node == null) return
postOrderTraverse(node.left)
postOrderTraverse(node.right)
console.log(node.value)
}3. 解题思路
- BST 中序遍历,即从小到大的排序
- 找到排序后的第 k 值即可
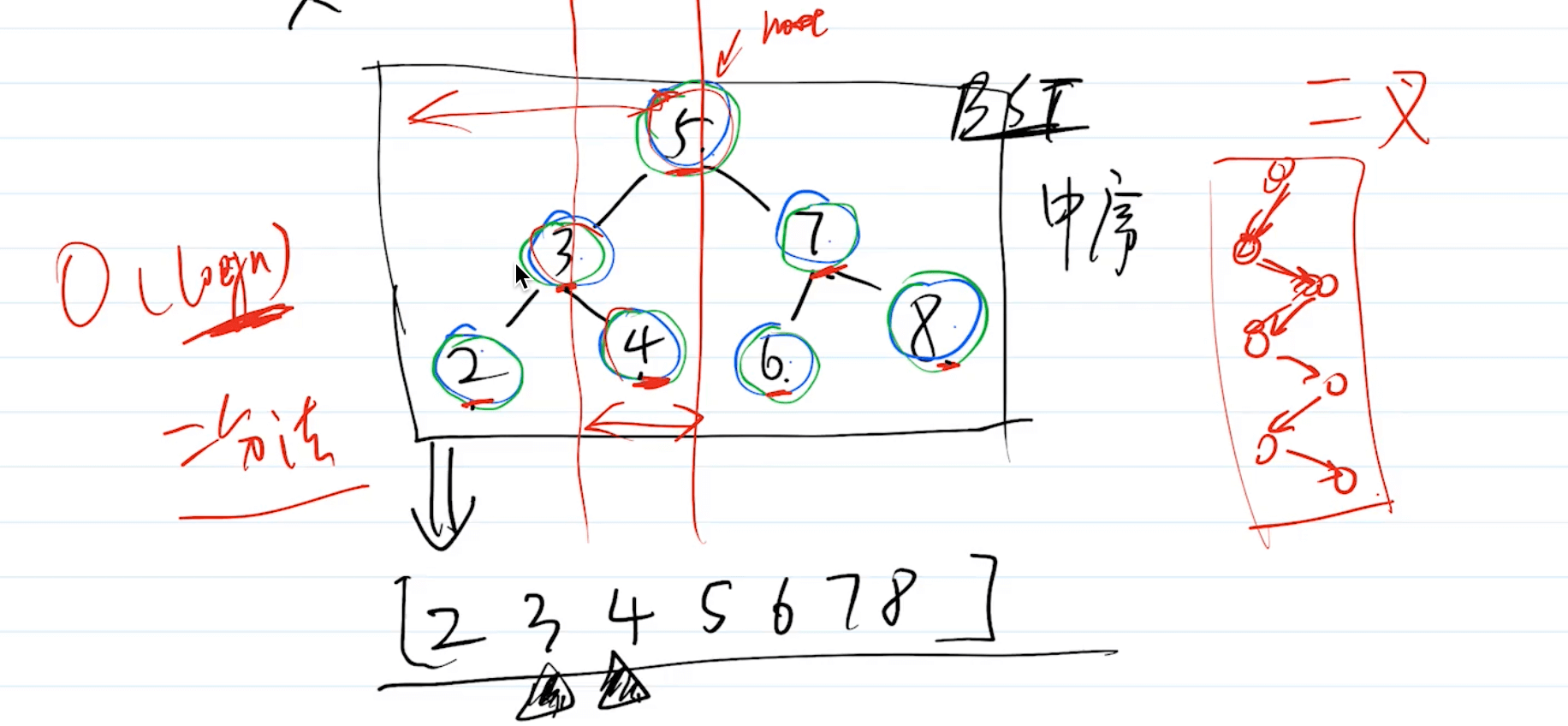
4. 代码
typescript
const array: number[] = []
/**
* 二叉树中序遍历
* @param node node
*/
function inOrderTraverse(node: TreeNode | null) {
if (node == null) return
inOrderTraverse(node.left)
array.push(node.value)
inOrderTraverse(node.right)
}
/**
* 寻找 BST 里的第 k 小值
* @param node node
* @param k k
*/
function getKthValue(node: TreeNode, k: number): number | null {
inOrderTraverse(node)
return array[k - 1] || null
}5. 单元测试
typescript
/**
* @description 二叉搜索树第 k 小值
* @author lzz
*/
import {bst, getKthValue} from "./8.求一个二叉搜索树的第 k 小值";
describe('二叉搜索树第 k 小值', () => {
it('正常情况', () => {
expect(getKthValue(bst, 3)).toBe(4)
});
it('k 不在正常范围之内', () => {
expect(getKthValue(bst, 0)).toBeNull()
expect(getKthValue(bst, 100)).toBeNull()
});
})6. 划重点
- 二叉树,和三种(前序、中序、后序)遍历
- 二叉搜索树的特点:left <= root; right >= root
- 二叉搜索树的价值:可使用 二分法 进行快速查找
二、为何二叉树如此重要,而不是其他叉树
1. 性能、性能还是性能
- 数组:查询快 O(1),增删慢 O(n)
- 链表:查询慢 O(n),增删快 O(1)
- 二叉搜索树 BST:查询快,增删快 -- “ 木桶效应 ”
2. 平衡二叉树
- BST 如果不平衡,那就又成了链表了
- 所有要尽量平衡:平衡二叉搜索树 BBST
- BBST 增删查,时间复杂度都是 O(logn),即树的高度
3. 红黑树
- 一种自平衡二叉树
- 分为 红/黑 两种颜色,通过颜色转换来维持树的平衡
- 相对于普通平衡二叉树,它维持平衡的效率更高
4. B 树
- 物理上是多叉树,但逻辑上是二叉树
- 一般用于高效 I/O,关系型数据库常用于 B树来组织数据
5. 小结
- 数组、链表,各有各的缺点
- 特定的二叉树( BBST )可以让整体效果最优
- 各种高级二叉树,继续优化,满足不同场景
三、堆有什么特点,和二叉树有什么关系
1. 堆栈模型
- JS 代码执行时
- 值类型变量,存储在栈
- 引用类型变量,存储在堆
2. 堆
- 完全二叉树
- 最大堆:父节点 >= 子节点
- 最小堆:父节点 <= 子节点

3. 逻辑结构 vs 物理结构
- 堆,逻辑结构 是一棵二叉树
- 但它 物理结构 是一个数组
- 数组:适合连续存储 + 节省空间( 回顾堆栈模型 )
4. 堆 vs BST
- 查询比 BST 慢
- 增删比 BST 快,维持平衡更快
- 但整体的时间复杂度都在 O(logn) 级别,即树的高度
5. 堆的使用场景
- 特别适合 “ 堆栈模型 ”
- 堆的数据,都是在栈中引用的,不需要从 root 遍历
- 堆恰巧是数组形式,根据栈的地址,可用 O(1) 找到目标
6. 小结
- 堆栈模型,堆的场景
- 堆的特点,堆和 BST
- 堆的逻辑结构和物理结构
四、求斐波那契数列第 n 个值
1. 题目
- 用 JS 计算斐波那契数列的第 n 个值
- 注意时间复杂度
2. 解题思路
- f(0) = 0
- f(1) = 1
- f(n) = f(n - 1) + f(n - 2)
3. 代码(递归,不可用)
typescript
/**
* @description 求斐波那契数列第 n 个值
* @author lzz
*/
/**
* 斐波那契数列第 n 个值(递归)
* @param n
*/
function fibonacci(n: number): number {
if (n <= 0) return 0
if (n === 1) return 1
return fibonacci(n - 1) + fibonacci(n - 2)
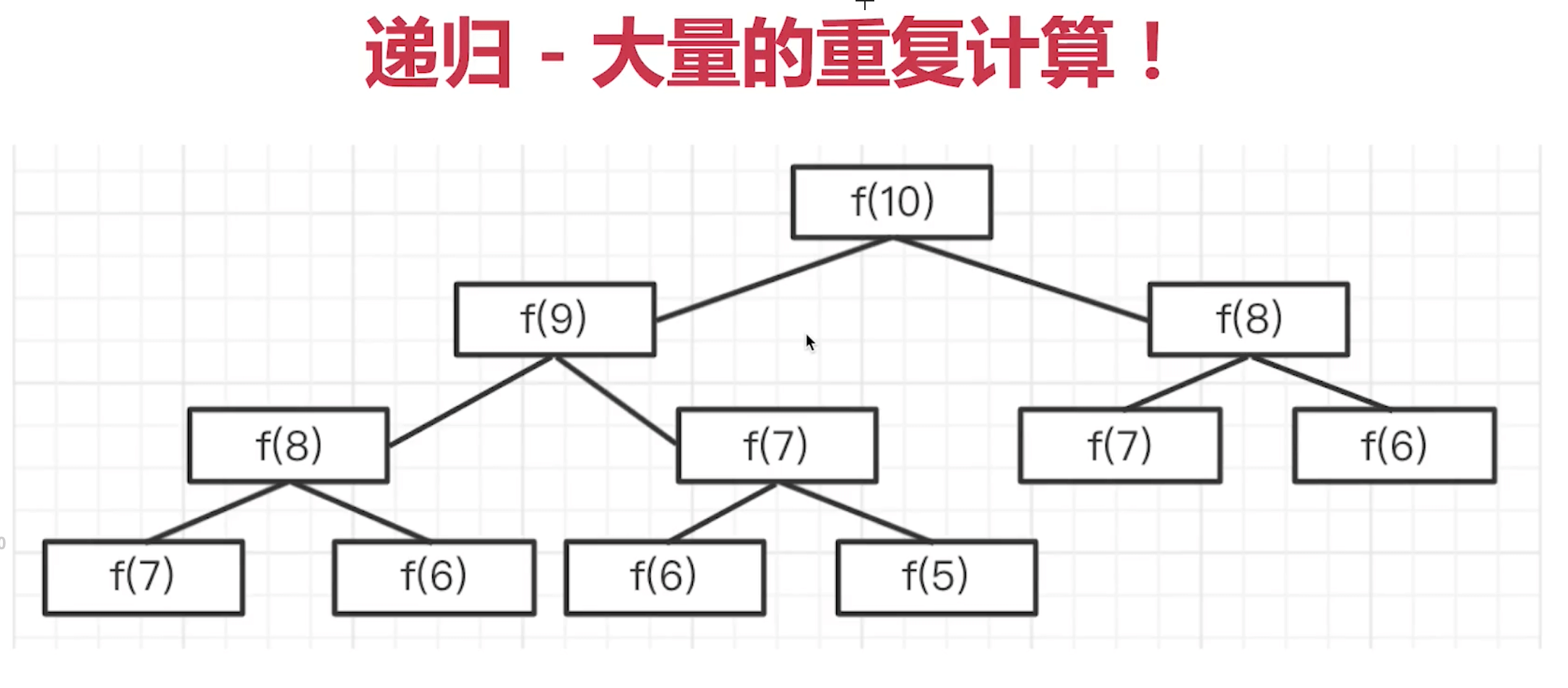
}4. 分析
- 递归 - 大量的重复计算!
- 时间复杂度是 O(2^n)
5. 优化
- 不用递归,用循环
- 记录中间结果
- 时间复杂度为 O(n)
6. 代码(循环)
typescript
/**
* 斐波那契数列第 n 个值 (循环)
* @param n
*/
function fibonacci(n: number): number {
if (n <= 0) return 0
if (n === 1) return 1
let n1 = 1 // 记录 n - 1 的结果
let n2 = 0 // 记录 n - 2 的结果
let res = 0
// 要从 2 开始循环
for (let i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
res = n1 + n2
// 记录中间结果
n2 = n1
n1 = res
}
return res
}7. 单元测试
typescript
/**
* @description 求斐波那契数列的第n值
* @author lzz
*/
import {fibonacci} from './9.求斐波那契数列的第n值'
describe('求斐波那契数列的第n值', () => {
it('0 和 1', function () {
expect(fibonacci(0)).toBe(0)
expect(fibonacci(1)).toBe(1)
});
it('除 0 和 1 外, 正常情况', function () {
expect(fibonacci(9)).toBe(34)
});
it('n 小于 0', function () {
expect(fibonacci(-1)).toBe(0)
});
})8. 动态规划
- 把一个大问题,拆解成多个小问题,逐级向下拆解
- 用递归的思路去分析问题,再改为循环来实现
- 算法三大思维:贪心、二分、动态规划
五、(连环问)青蛙跳台阶有几种方式
1. 题目
- 一只青蛙,一次可以跳 1 级,也可以跳 2 级
- 问:青蛙跳到 n 级台阶,总共有多少种方式?
2. 用动态规划分析问题
- 要跳到 1 级台阶,就 1 种方式 f(1) = 1
- 要跳到 2 级台阶,就 2 种方式 f(2) = 2
- 要跳到 n 级台阶,f(n) = f(n - 1) + f(n - 2)

- 和斐波那契数列完全一样
六、移动 0 到数组的末尾
1. 题目
- 如输入 [1, 0, 3, 0, 11, 0] ,输出 [1, 3, 11, 0, 0, 0]
- 只移动 0 ,其他顺序不变
- 必须在原数组进行操作
2. 如果不限制 “ 必须在原数组操作 ”
- 定义 part1 part2 两个数组
- 遍历数组,非 0 push 到 part1 ,0 push 到 part2
- 返回 part1.concat(part2)
3. 传统思路
- 遍历数组,遇到 0 则 push 到数组结尾
- 用 splice 截取掉当前元素
- 时间复杂度是 O(n^2) -- 算法不可用
4. 代码(传统思路)
typescript
/**
* @description 移动 0 到数组末尾
* @author lzz
*/
const array = [1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1]
/**
* 移动 0 到数组末尾 (传统思路: 嵌套循环)
* @param arr number arr
*/
function moveZero1(arr: number[]): void {
const len = arr.length
if (!len) return
let zeroLen = 0
// O(n^2)
for (let i = 0; i < len - zeroLen; i++) {
if (arr[i] === 0) {
arr.push(0)
arr.splice(i, 1) // 本身就有 O(n)
i-- // 数组截取了一个元素, i 要递减, 否则遇到连续 0 会有错误
zeroLen++ // 累计 0 的长度
}
}
return
}5. 双指针代码思路
- 定义 j 指向第一个 0 ,i 指向 j 后面的第一个非 0
- 交换 i 和 j 的值,继续向后移动
- 只遍历一次,所以时间复杂度是 O(n)
6. 代码(双指针)
typescript
/**
* 移动 0 到数组末尾 (双指针)
* @param arr
*/
function moveZero2(arr: number[]): void {
const len = arr.length
if (!len) return
let i
let j = -1 // 指向第一个 0
for (i = 0; i < len; i++) {
if (arr[i] === 0) {
// 第一个 0
if (j < 0) {
j = i
}
}
if (arr[i] !== 0 && j !== -1) {
// 交换
const temp = arr[i]
arr[i] = arr[j]
arr[j] = temp
j++
}
}
}7. 单元测试
typescript
/**
* @description 移动 0 到数组末尾
* @author lzz
*/
import {moveZero1, moveZero2} from "./10.移动 0 到数组末尾";
describe('移动 0 到数组末尾', () => {
it('正常类型', function () {
const array = [1, 0, 3, 4, 0, 11, 0]
moveZero2(array)
expect(array).toEqual([1, 3, 4, 11, 0, 0, 0])
});
it('连续 0 情况', function () {
const array = [1, 0, 3, 4, 0, 0, 0, 11, 0]
moveZero2(array)
expect(array).toEqual([1, 3, 4, 11, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0])
});
it('没有 0', function () {
const array = [1, 3, 4, 11]
moveZero2(array)
expect(array).toEqual([1, 3, 4, 11])
});
it('全是 0', function () {
const array = [0, 0, 0, 0]
moveZero2(array)
expect(array).toEqual([0, 0, 0, 0])
});
})8. 性能测试
typescript
const testArr = []
for (let i = 0; i < 20 * 10000; i++) {
i % 10 ? testArr.push(i) : testArr.push(0)
}
console.time('嵌套循环')
moveZero1(testArr)
console.timeEnd('嵌套循环') // 5.477s
console.time('双指针')
moveZero2(testArr)
console.timeEnd('双指针') // 3.22ms9. 划重点
- 向面试官确认:是否必须修改原数组?
- 数组是连续存储,要慎用 unshift 、splice 等 API
- 双指针思路
七、字符串中连续最多的字符,以及次数
1. 题目
- 如,输入 ‘ abbcccddeeee1234 ’ ,计算得到:
- 连续最多的字符是 ‘ e ’ ,4 次
2. 传统思路
- 嵌套循环,找出每个字符的连接次数,并记录
- 看似时间复杂度是 O(n^2)
- 但是实际时间复杂度是 O(n) ,因为有 “ 跳步 ”
3. 代码 ( 嵌套循环 )
typescript
/**
* 获取字符串中连续最多的字符及次数(嵌套循环)
* @param str
*/
function findContinuousChar1(str: string): IRes {
const res: IRes = {
str: '',
times: 0
}
const len = str.length
if (!len) return res
let tempLength = 0 // 临时记录当前连续字符的长度
// O(n)
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
tempLength = 0
for (let j = i; j < len; j++) {
if (str[i] === str[j]) {
tempLength++
}
if (str[i] !== str[j] || j === len - 1) {
// 不相等, 或者已经到了最后一个元素, 要判断最大值
if (tempLength > res.times) {
res.str = str[i]
res.times = tempLength
}
if (i < len - 1) {
i = j - 1 // 跳步
}
break
}
}
}
return res
}4. 双指针思路
- 定义指针 i 和 j ,j 不动,i 继续移动
- 如果 i 和 j 的值一直相等,则 i 继续移动
- 直到 i 和 j 的值不相等,记录处理,让 j 追上 i 。重复第一步
5. 代码(双指针)
typescript
/**
* 获取字符串中连续最多的字符及次数(双指针)
* @param str
*/
function findContinuousChar2(str: string): IRes {
const res: IRes = {
str: '',
times: 0,
}
const len = str.length
if (!len) return res
let tempLength = 0 // 临时记录当前连续字符的长度
let i
let j = 0
// O(n)
for (i = 0; i < len; i++) {
if (str[i] === str[j]) {
tempLength++
}
if (str[i] !== str[j] || i === len - 1) {
// 不相等, 或者已经到了最后一个元素, 要判断最大值
if (tempLength > res.times) {
res.str = str[j]
res.times = tempLength
}
tempLength = 0 // 重置
if (i < len - 1) {
j = i // 让 j 追上 i
i-- // 细节
}
}
}
return res
}6. 单元测试
typescript
/**
* @description 获取字符串中连续最多的字符及次数
* @author lzz
*/
import {findContinuousChar1, findContinuousChar2} from './11.获取字符串中连续最多的字符及次数'
describe('获取字符串中连续最多的字符及次数', () => {
it('正常情况', function () {
expect(findContinuousChar2('aabbcccddeeee11223')).toEqual({
str: 'e',
times: 4
})
});
it('空字符串', function () {
expect(findContinuousChar2('')).toEqual({
str: '',
times: 0
})
});
it('无连续', function () {
expect(findContinuousChar2('abcdefghijk')).toEqual({
str: 'a',
times: 1
})
});
it('全部连续', function () {
expect(findContinuousChar2('aaaaaaaaaaa')).toEqual({
str: 'a',
times: 11
})
});
})7. 性能测试
typescript
let str = ''
for (let i = 0; i < 100 * 10000; i++) {
str += i.toString()
}
console.time('findContinuousChar1')
findContinuousChar1(str)
console.timeEnd('findContinuousChar1'); // 159.09ms
console.time('findContinuousChar2')
findContinuousChar2(str)
console.timeEnd('findContinuousChar2'); // 150.831ms8. 其他方式
- 正则表达式 -- 效率非常低,慎用!!!
- 累计各个元素的连续长度,最后求最大值 -- 徒增空间复杂度
- PS:算法题尽量用 “ 低级 ” 代码,慎用语法糖或者高级 API
9. 划重点
- 要注意实际复杂度,不要被代码表面迷惑(类似于跳步)
- 双指针常用于解决嵌套循环
- 算法题慎用正则表达式(实际工作可以用)
八、用 JS 实现快速排序
1. 固定算法,固定思路
- 找到中间位置 midValue
- 遍历数组,小于 midvalue 放在 left ,否则放在 right
- 继续递归,最后 concat 拼接返回
2. 细节
- 获取 midValue 的两种方式:
- 使用 splice ,会修改原数组
- 使用 slice ,不会修改原数组 -- 更加推荐
3. 代码
typescript
/**
* @description JS 实现快速排序
* @author lzz
*/
/**
* 快速排序 - splice 方法
* @param arr
*/
function quickSort1(arr: number[]): number[] {
const len = arr.length
if (!len) return arr
const midIndex = Math.floor(len / 2)
const midValue = arr.splice(midIndex, 1)[0]
const left: number[] = []
const right: number[] = []
// 注意: 这里不能使用 len , 应使用 arr.length , 因为 splice 已经改变数组 arr
// O(nlogn)
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
const n = arr[i]
if (n < midValue) {
// 小于 midValue 则放在左侧
left.push(n)
} else {
// 大于 midValue 则放在右侧
right.push(n)
}
}
return quickSort1(left).concat(
[midValue],
quickSort1(right)
)
}
/**
* 快速排序 - slice 或 取索引 方法
* @param arr
*/
function quickSort2(arr: number[]): number[] {
const len = arr.length
if (!len) return arr
const midIndex = Math.floor(len / 2)
// 为了对比 splice , 可使用 arr[midIndex]
const midValue = arr.slice(midIndex, midIndex + 1)[0]
// const midValue = arr[midIndex]
const left: number[] = []
const right: number[] = []
// O(nlogn)
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
// 要忽略中间值
if (i !== midIndex) {
const n = arr[i]
if (n < midValue) {
// 小于 midValue 则放在左侧
left.push(n)
} else {
// 大于 midValue 则放在右侧
right.push(n)
}
}
}
return quickSort2(left).concat(
[midValue],
quickSort2(right)
)
}4. 单元测试
typescript
/**
* @description 快速排序
* @author lzz
*/
import {quickSort1, quickSort2} from './12. 快速排序'
describe('快速排序', () => {
it('正常情况 ', function () {
const arr = [1, 23, 2, 4, 4, 66, 7, 8]
expect(quickSort2(arr)).toEqual([1, 2, 4, 4, 7, 8, 23, 66])
});
it('有负数 ', function () {
const arr = [1, 23, -2, 4, 4, 66, 7, 8]
expect(quickSort2(arr)).toEqual([-2, 1, 4, 4, 7, 8, 23, 66])
});
it('同一元素 ', function () {
const arr = [1, 1, 1, 1, 1]
expect(quickSort2(arr)).toEqual([1, 1, 1, 1, 1])
});
it('空数组 ', function () {
expect(quickSort2([])).toEqual([])
});
})5. 时间复杂度
- 有遍历,有二分 -- O(nlogn)
- 常规排序,嵌套循环,复杂度是 O(n^2)
6. 性能测试
typescript
// 性能测试
const array = []
for (let i = 0; i < 10 * 10000; i++) {
array.push(Math.floor(Math.random() * 1000))
}
console.time('splice')
quickSort1(array)
console.timeEnd('splice') // 73.464ms
console.time('slice')
quickSort2(array)
console.timeEnd('slice') // 71.336ms7. splice 和 slice 没有区分出来
- 算法本身的时间复杂度就够高 O(nlogn)
- 外加,splice 是逐步二分之后执行的, 二分会快速消减数量级
- 如果单独比较 splice 和 slice ,效果会非常明显
8. 划重点
- 常见排序算法 -- 固定思维
- 有二分,时间复杂度就包含 O(logn)
- 注意数组操作:splice 和 slice
九、对称数
1. 题目
- 求 1-10000 之间所有的对称数(回文)
- 例如:1, 2, 11, 22, 101, 232, 1221...
2. 解题思路
- 思路一:使用数组反转、比较
- 数字转换为字符串,在转换为数组
- 数组 reverse ,再 join 为字符串
- 前后字符串进行对比
- 思路二:字符串头尾比较
- 数字转换为字符串
- 字符串头尾字符比较
- ( 也可以用 栈 ,像括号匹配,但要注意奇偶数 )
- 思路三:生成翻转数
- 使用 % 和 Math.floor 生成反转数
- 前后数字进行对比
- ( 全程操作数字,没有字符串类型 )
3. 代码
typescript
/**
* 求 1-max 之间所有的对称数 - 反转比对
* @param max 最大值
*/
function palindromeNum1(max: number): number[] {
const res: number[] = []
if (max <= 0) return res
for (let i = 1; i <= max; i++) {
const str = i.toString()
// 转换为字符串,转换为数组,再反转,比较
if (str === str.split('').reverse().join('')) {
res.push(Number(str))
}
}
return res
}
/**
* 求 1-max 之间所有的对称数 - 字符串前后比对
* @param max 最大值
*/
function palindromeNum2(max: number): number[] {
const res: number[] = []
if (max <= 0) return res
for (let i = 1; i <= max; i++) {
const str = i.toString()
const len = str.length
let index = 0
for (let j = 0; j < len; j++) {
if (str[j] === str[len - 1 - j]) {
index++
}
}
if (index === len) res.push(i)
}
return res
}
/**
* 求 1-max 之间所有的对称数 - 生成反转数
* @param max 最大值
*/
function palindromeNum3(max: number): number[] {
const res: number[] = []
if (max <= 0) return res
for (let i = 1; i <= max; i++) {
let n = i
let rev = 0 // 储存反转数
// 生成反转数
while (n > 0) {
rev = rev * 10 + n % 10
n = Math.floor(n / 10)
}
if (i === rev) res.push(i)
}
return res
}4. 单元测试
typescript
/**
* @description 求 1-10000 之间所有的对称数(回文)
* @author lzz
*/
import {palindromeNum1, palindromeNum2, palindromeNum3} from './13.对称数'
describe('对称数', () => {
it('正常情况 ', function () {
expect(palindromeNum1(100).length).toBe(18)
});
it('max 小于等于 0 ', function () {
expect(palindromeNum1(0)).toEqual([])
});
})5. 性能测试
typescript
// 性能测试
console.time('palindromeNum1')
palindromeNum1(100 * 10000)
console.timeEnd('palindromeNum1') // 346ms
console.time('palindromeNum2')
palindromeNum2(100 * 10000)
console.timeEnd('palindromeNum2') // 106ms
console.time('palindromeNum3')
palindromeNum3(100 * 10000)
console.timeEnd('palindromeNum3') // 39ms6. 性能分析
- 思路1 - 看似是 O(n) ,但数组转换、操作都需要时间,所以慢
- 思路2 vs 思路3 ,操作数字更快(电脑原型就是计算器)
- 思路2 要用栈,不合适。因为栈也一般用数组实现,会慢
7. 划重点
- 尽量不要转换数据结构,尤其数组这种有序结构
- 尽量不要用内置 API ,如 reverse ,不好识别复杂度
- 数字操作最快,其次是字符串
十、高效的字符串前缀匹配
1. 题目
- 有一个英文单词库(数组),里面有十几万个英文单词
- 输入一个字符串,快速 判断是不是某一个单词的前缀
- 说明思路,不用写代码
2. 解题思路
- 常规思路
- 遍历单词库数组
- indexOf 判断前缀
- 实际时间复杂度超过了 O(n) ,因为要考虑 indexOf 的计算量
- 优化
- 英文字母一共 26 个,可以提前把单词库数拆分成 26 个
- 既然第一层拆分 26 个,第二层、第三层,还可以继续拆分
- 最后把单词库拆分成一棵树
3. 性能分析
- 如遍历数组,时间复杂度至少 O(n) 起步( n 是数组长度 )
- 而改成数,时间复杂度降低到 O(m) ( m 是单词长度 )
- PS:哈希表(对象)通过 key 查询,时间复杂度是 O(1)
4. 划重点
- 考虑优化原始数据结构(需先沟通)
- 有明确范围的数据(如 26 个英文字母),考虑使用哈希表(对象)
- 以空间换时间,定义数据结构最重要
十一、数字千分位格式化
1. 题目
- 将数字千分位格式化,输出字符串
- 如输入数字 12050100 ,输出字符串 12,050,100
- ( 注意:逆序判断 )
2. 常见思路
- 转换为数组,reverse ,每 3 位拆分
- 使用正则表达式
- 使用字符串拆分
3. 代码
typescript
/**
* @description 数字千分位格式化
* @author lzz
*/
/**
* 千分位格式化(使用数组)
* @param n
*/
export function format1(n: number): string {
n = Math.floor(n) // 只考虑整数部分
const s = n.toString()
const arr = s.split('').reverse()
return arr.reduce((prev, val, index) => {
if (index % 3 === 0) {
if (prev) {
return val + ',' + prev
} else {
return val
}
} else {
return val + prev
}
}, '')
}
/**
* 千分位格式化(使用字符串)
* @param n
*/
export function format2(n: number): string {
const num = Math.floor(n)
const str = num.toString()
const len = str.length
let res = ''
for (let i = len - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
const j = len - i
if (j % 3 === 0 && i !== 0) {
res = ',' + str[i] + res
} else {
res = str[i] + res
}
}
return res
}4. 单元测试
typescript
/**
* @description 数字千分位格式化
* @author lzz
*/
import {format1, format2} from './14.数字千分位格式化'
describe('数字千分位格式化', () => {
it('正常情况', function () {
expect(format2(100200300)).toBe('100,200,300')
});
it('千位以下', function () {
expect(format2(0)).toBe('0')
expect(format2(100)).toBe('100')
});
})5. 性能分析
- 使用数组,转换影响性能
- 使用正则表达式,性能较差
- 使用字符串,性能较好 -- 推荐答案
6. 划重点
- 顺序:从尾到头
- 尽量不要转化数据结构
- 慎用正则表达式
十二、切换字母大小写
1. 题目
- 输入一个字符串,切换其中字母的大小写
- 如,输入字符串 12aBc34 ,输出字符串 12AbC34
2. 常见思路
正则表达式
通过 ASCII 码判断
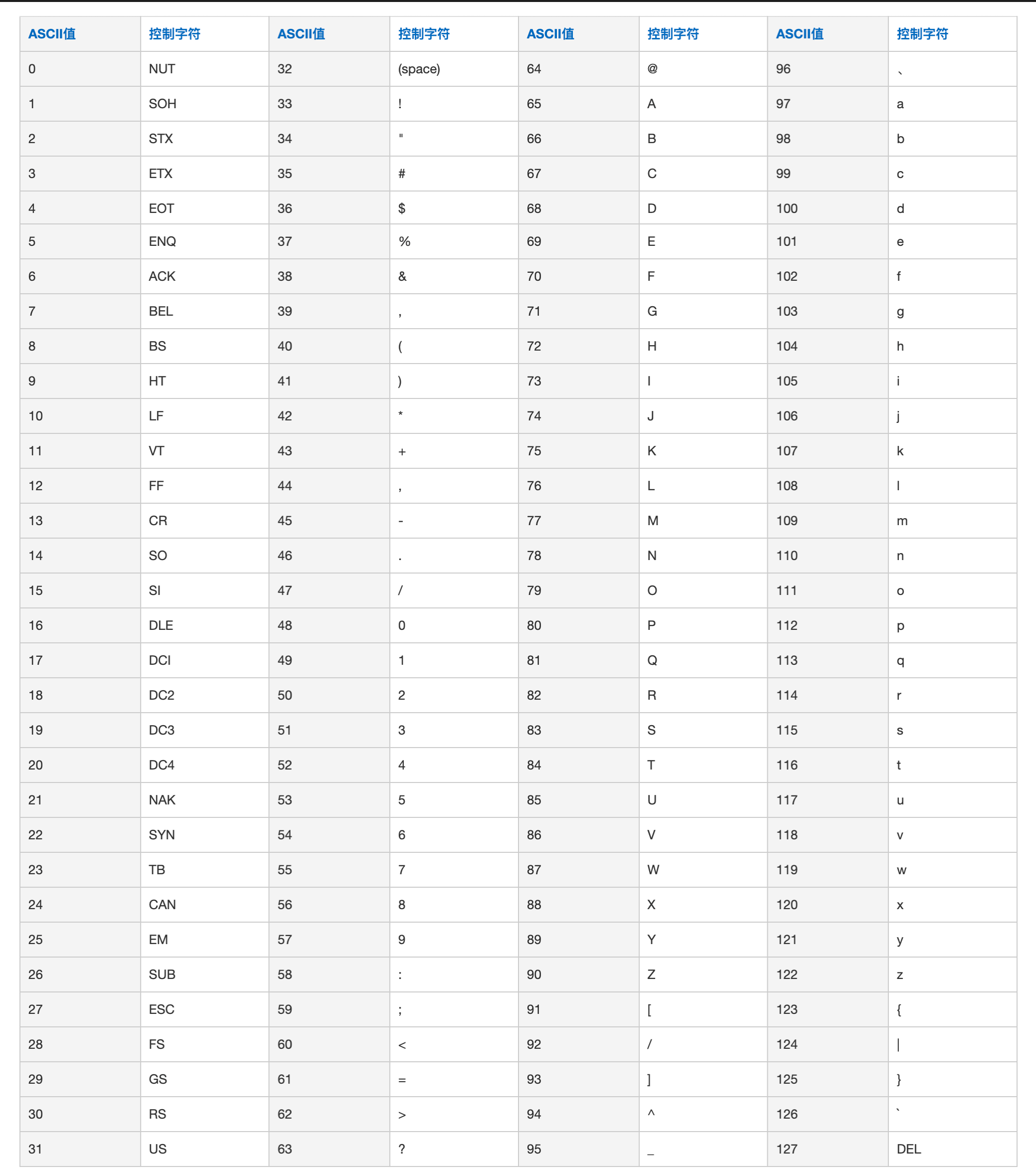
3. 代码
typescript
/**
* @description 切换字母大小写
* @author lzz
*/
/**
* 切换字母大小写 - 正则
* @param str
*/
function changeCase1(str: string): string {
let res = ''
const reg1= /[a-z]/
const reg2= /[A-Z]/
for (let i = 0; i < str.length; i++) {
if (reg1.test(str[i])) {
// 小写字母
res += str[i].toUpperCase()
} else if (reg2.test(str[i])) {
// 大写字母
res += str[i].toLowerCase()
} else {
res += str[i]
}
}
return res
}
/**
* 切换字母大小写 - ASCII
* @param str
*/
function changeCase2(str: string): string {
let res = ''
for (let i = 0; i < str.length; i++) {
const code = str[i].charCodeAt(0)
if (code >= 65 && code <= 90) {
// 大写字母
res += String.fromCharCode(code + 32)
// 也可使用 API 但是经过测试 会比上面方法慢
// res += str[i].toLowerCase()
} else if (code >= 97 && code <= 122) {
// 小写字母
res += String.fromCharCode(code - 32)
// res += str[i].toUpperCase()
} else {
res += str[i]
}
}
return res
}4. 单元测试
typescript
/**
* @description 切换字母大小写
* @author lzz
*/
import {changeCase1, changeCase2} from './15.切换字母大小写'
describe('切换字母大小写', () => {
it('正常情况', function () {
expect(changeCase2('2aBcD1')).toBe('2AbCd1')
});
it('空字符', function () {
expect(changeCase2('')).toBe('')
});
it('非字母', function () {
expect(changeCase2('2你!#')).toBe('2你!#')
});
})5. 性能测试
typescript
const s = '123asd321BhS33BSC'
console.time('reg')
for (let i = 0; i < 100 * 10000; i++) {
changeCase1(s)
}
console.timeEnd('reg') // 875ms
console.time('ascii')
for (let i = 0; i < 100 * 10000; i++) {
changeCase2(s)
}
console.timeEnd('ascii') // 224ms6. 性能分析
- 使用正则,性能较差
- 使用 ASCII 码,性能较好 -- 推荐答案
7. 划重点
- 慎用正则表达式
- 掌握常见的 ASCII 码
十三、为什么 0.1 + 0.2 !== 0.3
1. 计算机使用二进制存储数据
- 整数转换二进制没有误差,如 9 转换为二进制是 1001
- 而小数可能无法用二进制准确的表达,如 0.2 转换为 1.1001100...
- 不光 JavaScript 其他编程语言也如此
总结
1. 内容总结
- 前端数据结构和算法的常见题目
- 包含了数组、栈、队列、链表、二叉树这些常见的数据结构
- 常用的算法思维如贪婪、二分、动态规划,以及如何计算时间复杂度
2. 划重点
- 有序数据考虑用二分
- 双指针可以解决嵌套循环
3. 注意事项
- 注意区分逻辑结构和物理结构,否则思维会很混乱
- 要有 “算法敏感度”,条件反射般的根据数据结构分析时间复杂度